ETFs an exclusive form of investment
ETFs have gained wide acceptance as a financial instrument worldwide. However, in India, many investors are getting to know about this passively managed investment vehicle. As ETFs are the fastest growing markets in the world a lot are yet unaware of its benefits and opportunity to diversification. Read on…
What is ETFs?
Exchange traded funds are essential Index Funds that are listed and traded on the exchange. This has opened a whole new investment opportunity for individuals. As it broadens the exposure of entire markets in different sectors, at lower cost and on real-time basis. It is based on the net asset value of the underlying stocks. The buy and sell of ETF is simple, and many can take the advantage of intra-day price movements. Another advantage noticed is by just purchasing 1 unit of ETF, you get an exposure towards an entire index at a lower rate. One can seek the benefit of flexibility towards stocks and diversification of an open ended mutual fund scheme.
Structure of an ETF:
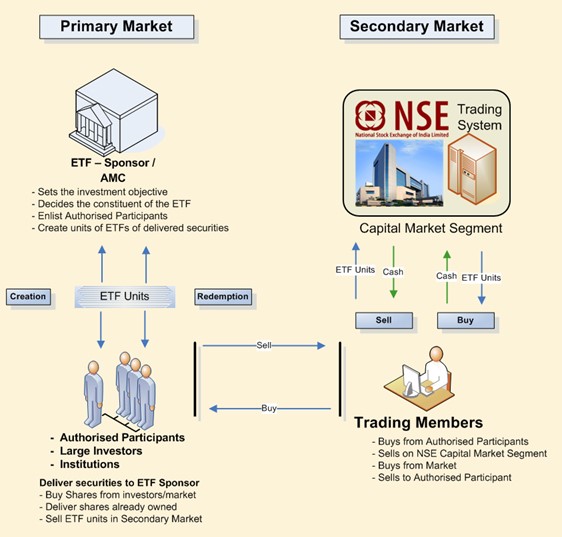
Source: NSE website
In the primary market, AMCs that sponsors ETFs, take shares of companies comprising index from various categories of investors and institutions to issue blocks of ETFs. There is no limit on the number of outstanding ETF units as compared to mutual funds. Shares could increase and decrease accordingly instructions given to fund house for creation and redemption of ETF units of the underlying shares. Trading members at the other corner trade in those ETF shares on the secondary markets. Secondary market trading is simple as there are buyers and sellers and according to the price preference investors Bid and Ask on the specific stock.
Authorized Participants: It’s a large institutional investor that enters into a contract to create ETFs.
Sponsors: The one who issues ETFs.
Creation: The process in which Authorized Participants sell stocks to the ETF sponsors in return for shares in an ETF is called creation.
Redemption: The process in which Authorized Participants buys the stocks from the ETF sponsors in return giving back the shares of the ETF is called redemption.
Active investment: Active investors try to beat the stock market average returns and take the advantage of short term price fluctuation.
Passive investment: Passive investors track the market. They mainly limit the amount of buying and selling within their portfolio, making this a cost effective way to invest.
Benefits of ETF:
- Entry and exit of the fund is applicable during trading hours
- Lower expense ratio than any other funds
- Easy purchases just like the other equity stocks
- Transparency in the stocks
- ETFs are liquidable
- Portfolio diversifier
- Low risk as invested in bulk of stocks (index)
Types of ETFs:
Index ETF - Index Exchange Traded Funds are the oldest and most common of the ETF product offerings. Index ETFs acquires securities in amounts that proportionately reflect the securities of an existing index in a given market. By investing in them an investor can get the benefit of broad diversification that replicates the performance of the underlying index.
Liquid ETFs - These investments are mainly in call money, short-term government securities and money market instruments of short maturities while maintaining safety and liquidity.
International ETFs - These are globally equity exchange traded funds, where the domestic investors are exposed to the international markets. At times when Indian equities aren’t performing well, US equities could be of benefit that could provide stability to the portfolio.
Bank ETF - Theses ETFs includes bank stocks listed on the index. They are highly traded and offer liquidity of which one can easily trade in margins. As the bank is the main route for financial activities like currency market, credits and many more. Demand for banking sector and ETFs is generally rising due to increase working population, growing disposable incomes, effective operational banking facilities and credible monitoring done by Reserve bank of India.
Commodity ETFs - ETFs are not only trading in stocks, but has extended to commodities where the underlying value is commodity itself. This ETF tracks the performance of the commodity index that includes number of underlying commodities, including the mixture of physical storage and derivative positions. In India, the most favoured commodity are gold and many are investing in gold ETFs because of its advantage of hedging over inflation.
Gold ETFs - These ETFs hold physical gold as their underlying asset. The returns are low in this ETF but due to their safe investment for long term they are yet popular among the investors. In total 13 gold ETFs are available in India as of 2019, the performance of these funds largely based on the physical gold price. The price of the gold ETF would be close to the real value of the physical gold. The charges applied in a gold ETF are expense ratio that is lower than a mutual fund and brokerage charges on the buy and sell of the stock. In comparison, between gold ETF and physical gold, ETFs save on the storage risk, flexible, liquid able and tax efficient. Gold ETFs are a risk diversifier that protects your investments from inflation and currency fluctuations.
The first Gold ETF was launched in India 2007 with the name of Gold BeES and now the value of gold has grown to 19% per annum that is between 2009-17 crossing 5 trillion-dollar. In a way investors get the opportunity to save, in gold without having the security risk and locker charges to be paid. Gold ETFs are passive investment that is based on the price movement and investments in physical gold.
ETF Bonds - Bonds ETFs were the addition in the Indian markets. What is a Bond ETF? It is basically trading in bonds via the exchange just like any conventional bond mutual fund. But these bond ETFs will be more transparent, liquid and cheaper. They fall into 4 categories; corporate, sovereign, government and broad market. Some ETFs would track based on credit quality or maturity and other based on geographical region or industry.
Bharat bond ETFs – India’s first debt ETF has broadened the bond markets and has given the opportunity for individual’s participation. This, ETF has a defined maturity, i.e. it will mature after a fixed period. Similar to close ended mutual funds, the units are listed on the stock exchange. This ETF features only growth option and no dividend option is availed. This bond provides stable returns at maturity and is safe as the investments are into public sector bonds. It is taxed at 20% post indexation excluding surcharges. There is transparency in the performance as the NAV and the portfolio is disclosed daily.
Smart beta ETFs – This index has stocks picked with low volatility, alpha, quality and value. They are a combination of active and passive investment strategy.
Taxes on ETFs:
For long term (more than 36 months), capital gains are taxed at 20% with indexation and for short term (up to 36 months), capital gains are added to income and taxed as per income slab.
Is it a must to have ETF in your portfolio?
One of the advantage that an ETF has over the portfolio is targeting multiple stocks under one fund that is traded on the exchange. Diversification is the tool as it gives an exposure to various industries and sectors across. With variety options available to ETFs one could hedge its portfolio risk by adding commodity ETF to beat inflation or utilize the inverse ETFs when the market is against your favour. Tracking down a list of stocks gets difficult and investing in index funds through ETF mode enables the investors to broaden its market.
Things to consider before buying an ETF
Investment objective and term
The purpose of an investment is the most basic and important aspect to factor in. Why are you opting for ETFs? Are you targeting a particular sector or industry? Are you trying to hedge against market volatility? It is easier to pick the right ETF when you have firm & clear objective behind investing. Same goes for investment horizon. Some ETFs produce above average returns in the long haul while some are suitable for short run only. Determining the investment period is thus equally crucial.
Cost
Although cost effectiveness is one of the advantages ETFs over mutual funds, all ETFs are not uniformly charged. Two ETFs may track same index but differ in management fees. However, marginal the difference, it's better to take everything from trading fees to operating commission into consideration.
Liquidity
Liquidity of an ETF depends on three elements – trading volume, fund's composition and financial environment. Trading volume refers to the number of times a particular security is traded during given trading period. The more the trading volume, the better chances of selling or redeeming your funds. In this case, trading volume of underlying securities (individual) as well as of the entire ETF basket affect fund's liquidity.
Composition of ETF means the structure or basis on which an ETF is built. Asset class, market capitalization, sector are a few categories of ETF composition. For example, an ETF focusing on equity asset has more liquidity than a real estate ETF. Similarly, ETFs that invest in large-cap companies are more liquid than their peer funds. This is because large-cap companies are more popular among investors, and their stocks experience higher demand than mid or small cap stocks.
As for financial environment, companies in developed nations are likely to give safer returns than companies in an emerging economy. ETF investing in these secure environment are apt for a person with moderate or conservative risk appetite. A side benefit is that ETFs that track broad market indices are less volatile than those focusing on a particular sector. All in all, ETFs investing in broad market indices, large cap companies& liquid assets ensure easy liquidity. And this level of liquidity impacts profitability of the ETF.
Benchmark
When choosing an ETF, first decide on the market, market segment, or industry sector you wish to track, then decide on the appropriate index for that market. Each index provider has its own construction methodology, resulting in wide variations in turnover and other portfolio characteristics. Benchmarks tracking the same market segment can deliver very different results.
Management Team
Index funds are not created equal. Effective, efficient portfolio management skills can make a difference, often offsetting marginal differences in costs between two indexed products. Review the experience and track record of the fund managers.
Summing up
ETFs have been captured in all the sections of the market, giving investors variety of options to trade in the market hours. It is a portfolio diversifier and investors who seek for long term investment would think over a switch from a mutual fund to an exchange traded fund.
ICICI Securities Ltd.( I-Sec). Registered office of I-Sec is at ICICI Securities Ltd. - ICICI Venture House, Appasaheb Marathe Marg, Prabhadevi, Mumbai - 400025, India, Tel No:- 022 - 2288 2460, 022 - 2288 2470. I-Sec is a Member of National Stock Exchange of India Ltd (Member Code:-07730) and BSE Ltd (Member Code :103) and having SEBI registration no. INZ000183631. Name of the Compliance officer (broking): Ms. Mamta Shetty, Contact number: 022-40701000, E-mail address: complianceofficer@icicisecurities.com. Investment in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. The contents herein above shall not be considered as an invitation or persuasion to trade or invest. I-Sec and affiliates accept no liabilities for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of any actions taken in reliance thereon.
Global Investment Platform is offered by ICICI Securities in collaboration with interactive brokers. Involvement of ICICI Securities Ltd. is restricted to Referral Only. ICICI Securities Ltd. does not offer this product directly to customers. Client’s details will be shared with third party stock broker (Interactive Brokers Group, Inc.) with expressed consent from clients. All dealings including KYC will be executed by third party stock broker (Interactive Brokers Group, Inc.) directly with client and ICICI Securities Ltd. will not incur any personal financial liability. All disputes with respect Global Investment will not have exchange redressal and arbitration mechanism.








Happy Reading!